Installation
1. Preparation
To successfully install StreamPark, the following environments need to be prepared:
| Item | Version | Required | Other |
| Operating System | Linux/MacOS | Windows is not supported | |
| Java | 1.8+ | Java version >=1.8 | |
| Scala | 2.12+ | Scala version >=2.12 | |
| Database | MySQL: 5.6+, Postgresql: 9.6+ | Defaults to H2 database, supports MySQL and Postgresql | |
| Flink | 1.12+ | Minimum supported Flink version is 1.12 | |
| Hadoop | 2+ | Optional, required for YARN deployment | |
| Kubernetes | 1.16+ | Optional, required for Kubernetes deployment |
2. Download
You can download the latest version of StreamPark directly from the official website. The version used in this document is 2.1.5, available at: https://streampark.apache.org/download
After the download is complete, extract the package:
# Extract the StreamPark installation package.
tar -zxvf apache-streampark_2.12-2.1.5-incubating-bin.tar.gz
The extracted directory will look like this:
├── bin
│ ├── startup.sh // Startup script
│ ├── shutdown.sh // Shutdown script
│ └── ......
├── conf
│ ├── config.yaml // Project configuration file
│ └── logback-spring.xml // Logging configuration file
├── lib
│ └── *.jar // Project JAR files
├── logs // Log directory
├── script
│ ├── data
│ │ ├── mysql-data.sql // MySQL DDL SQL scripts
│ │ └── pgsql-data.sql // PostgreSQL DDL SQL scripts
│ ├── schema
│ │ ├── mysql-schema.sql // MySQL full initialization data
│ │ └── pgsql-schema.sql // PostgreSQL full initialization data
│ └── upgrade
│ ├── mysql
│ │ ├── 1.2.3.sql // SQL script for upgrading to version 1.2.3
│ │ ├── 2.0.0.sql // SQL script for upgrading to version 2.0.0
│ │ ├── ......
│ └── pgsql
│ └── ......
└── temp // Temporary directory for internal use, do not delete
3. Start
Navigate to the bin directory under the installation directory and start the program:
# Go to the bin directory under the installation directory
cd bin
# Start the program
./startup.sh
After starting the program, you may encounter the following error:
streampark.workspace.local: "/tmp/streampark" is an invalid path, please reconfigure in xxx/conf/config.yaml
This is because the local workspace directory for StreamPark does not exist or is not set to a valid path. The solution is simple: you can use the default configuration and create the streampark directory under /tmp:
mkdir -p /tmp/streampark
Alternatively, configure a valid local path in the streampark.workspace.local property in the conf/config.yaml file.
Run startup.sh again, and you should see that the program starts successfully:
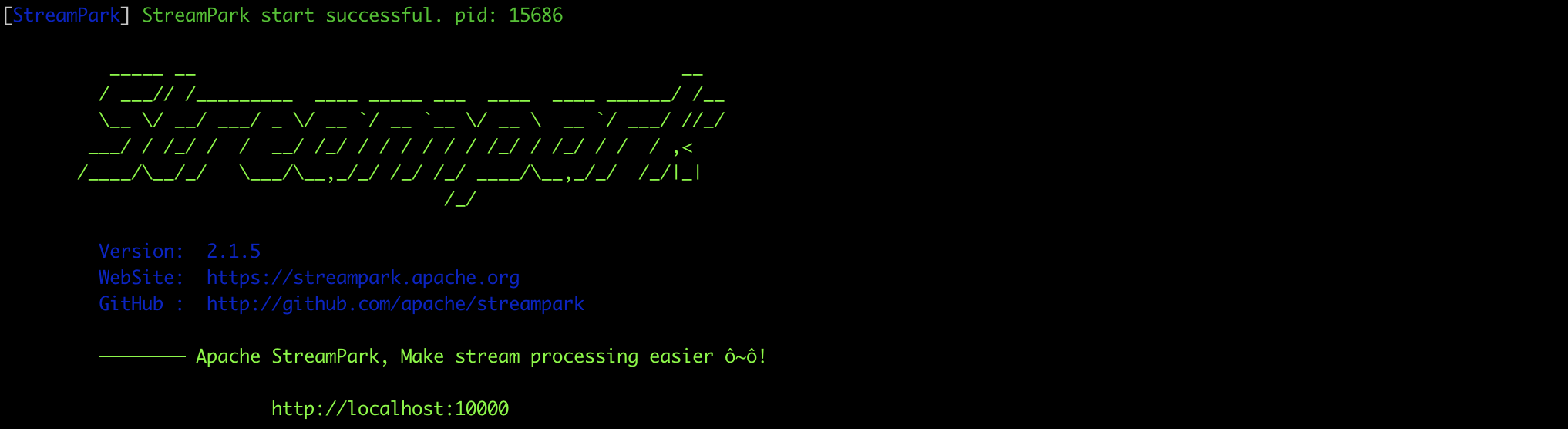
Visit StreamPark at: http://127.0.0.1:10000
Username and password: admin / streampark
You should see Login successful!
4. More
At this point, you can see that the project is running successfully. The installation above is based on the default H2 local database. Let’s now look at how to integrate external databases (MySQL or PostgreSQL).
4.1 Use External Database
If you want to use an external database, you need to modify the conf/config.yaml file in the installation directory. The core modification is as follows (using MySQL as an example):
datasource:
dialect: mysql # Change this to mysql, default is h2, supports mysql and pgsql
h2-data-dir: ~/streampark/h2-data # If using H2, configure this directory. If using MySQL or PostgreSQL, configure the remaining information (username and password)
username: # Username for the data source connection
password: # Password for the data source connection
url: # JDBC connection URL, e.g., jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/streampark?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&useJDBCCompliantTimezoneShift=true&useLegacyDatetimeCode=false&serverTimezone=GMT%2B8
Next, manually connect to the external database and initialize the MySQL table creation script (location: installation_directory/script/schema/mysql-schema.sql) and the data initialization script (location: installation_directory/script/data/mysql-data.sql).
Once the above steps are complete, start the service, and it will automatically connect and use the external database.
4.2 Use Hadoop
If you need to deploy jobs to YARN, you must configure the Hadoop environment variables. If you are using a Hadoop environment installed via CDH, the relevant environment variables can be configured as follows:
export HADOOP_HOME=/opt/cloudera/parcels/CDH/lib/hadoop # Hadoop installation directory
export HADOOP_CONF_DIR=/etc/hadoop/conf
export HIVE_HOME=$HADOOP_HOME/../hive
export HBASE_HOME=$HADOOP_HOME/../hbase
export HADOOP_HDFS_HOME=$HADOOP_HOME/../hadoop-hdfs
export HADOOP_MAPRED_HOME=$HADOOP_HOME/../hadoop-mapreduce
export HADOOP_YARN_HOME=$HADOOP_HOME/../hadoop-yarn
StreamPark will automatically read the Hadoop configuration from the environment variables, connect to Hadoop, upload resources to HDFS, and deploy jobs to YARN.
In addition, you may need to modify the conf/config.yaml file (for example, specifying the hadoop user, Kerberos authentication, etc.). The core modifications are as follows:
streampark:
workspace:
# Root path for storing resources in HDFS
remote: hdfs:///streampark/
proxy:
# Hadoop YARN proxy URL, e.g., Knox process address https://streampark.com:8443/proxy/yarn
yarn-url:
yarn:
# Authentication type
http-auth: 'simple' # Default is simple or kerberos
# Flink on YARN or Spark on YARN, HADOOP_USER_NAME
hadoop-user-name: hdfs
# If Kerberos authentication is enabled, configure the following:
security:
kerberos:
login:
debug: false
enable: false
keytab:
krb5:
principal:
4.3 Other Configurations
Here is the detailed explanation of the config.yaml file configuration, allowing you to easily integrate SSO or LDAP, etc.:
########################################### Logging Configuration ###########################################
logging:
level:
root: info
########################################### Basic Service Configuration ###########################################
server:
port: 10000
session:
ttl: 2h # User login session expiration time. Users will be automatically logged out after this period.
undertow: # Undertow service settings
buffer-size: 1024
direct-buffers: true
threads:
io: 16
worker: 256
########################################### Database Configuration ###########################################
datasource:
dialect: h2 # Database dialect, supports h2, mysql, pgsql
h2-data-dir: ~/streampark/h2-data # If using H2, configure this directory
username:
password:
url: # Database connection URL, e.g., jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/streampark?......
########################################### Project Configuration ###########################################
streampark:
## Workspace configuration, local and HDFS workspaces for different types of resources
workspace:
local: /tmp/streampark
remote: hdfs:///streampark/
## Proxy settings
proxy:
lark-url: # Feishu proxy URL
yarn-url: # YARN proxy URL
## YARN-related configuration
yarn:
http-auth: 'simple' # Authentication method
hadoop-user-name: hdfs # Configure the Hadoop username
## Project management settings
project:
max-build: 16 # Maximum number of projects to run concurrently.
## Development interface settings
openapi:
white-list: # Configure the white list for open APIs
########################################### Kerberos Authentication Configuration ###########################################
security:
kerberos:
login:
debug: false
enable: false
keytab:
krb5:
principal:
ttl: 2h
########################################
Looking forward to your further exploration~